What is OTA in software engineering, and why has it become such a fundamental part of how modern software evolves?
If you’ve ever opened your phone in the morning and noticed that an app feels faster, looks cleaner, or behaves differently — even though you didn’t install anything — you’ve likely experienced OTA in action.
Today, OTA (Over-the-Air) updates are one of the quiet engines behind software reliability. They let teams deliver improvements instantly, fix bugs without waiting for user action, and evolve their products continuously.
What Is OTA? A Clear and Simple Definition
OTA stands for Over-the-Air, a method that allows devices to receive software updates wirelessly, using only an internet connection.
Here’s the simplest way to picture it:
- No cables
- No manual download
- No complicated installation steps
- Minimal or zero user interaction
Everything happens silently in the background.
For software teams, this is a massive advantage. OTA behaves like a steady maintenance tool that keeps the product updated, secure, and healthy — even when users don’t notice it.
Why OTA Matters in Software Engineering
OTA has grown from a convenience feature to a necessity. Let’s break down why.
1. It eliminates friction for users
Most users prefer technology that “just works.”
OTA updates support exactly that.
Imagine telling millions of users to download a patch manually. Almost none would do it quickly.
OTA ensures:
- updates reach everyone,
- no one needs technical knowledge,
- adoption is nearly automatic.
This makes OTA ideal for long-tail queries like mobile OTA update process — people want updates with as little friction as possible.
2. It allows instant security fixes
Software vulnerabilities happen — even in the best systems.
What matters is how fast you respond.
With OTA:
- security patches can be deployed immediately,
- every device receives the fix quickly,
- risks are minimized before they grow.
In an age where security issues can spread rapidly, OTA gives developers a powerful shield.
3. It supports controlled and safe rollout strategies
Modern software teams rarely push an update to everyone at once.
Instead, they rely on gradual rollout, sometimes called “canary releases.”
OTA enables you to update:
- first, a small group of users,
- then a larger audience,
- and finally the entire user base.
This approach reduces risk and is a key component of OTA update management, another common long-tail search topic.
4. It provides a clean rollback option
Even well-tested updates can sometimes introduce issues.
OTA makes rollback simple:
- detect the issue,
- revert to the previous stable version,
- deploy that rollback OTA to all devices.
Recovery becomes smoother, faster, and far less damaging to user experience.
How OTA Updates Work (a friendly, digestible explanation)
The underlying system for OTA updates can be complex, but the high-level flow is easy to understand. Here’s what typically happens:
- Developers build a new version.
Bugs fixed, features improved, performance tuned. - The update is packaged and uploaded to a secure OTA server.
This server governs who receives what update and when. - Devices periodically check in.
“Is there an update available for me?” - If yes, the update download begins silently.
No pop-ups, no effort, users continue their work. - The update installs itself.
Sometimes instantly, sometimes after a restart.
On mobile, this may happen while the device is idle. - The user enjoys a fresher, safer version.
Many never realize an update even occurred.
Bu kadar basit — arka planda düzenli çalışan bir bakım sistemi gibi.
Where OTA Systems Are Used Today
OTA is not just for smartphones. It’s now embedded in many layers of software engineering.
Mobile applications
Most mobile platforms rely heavily on OTA to deliver system updates and app improvements.
Desktop applications
Tools like Electron or macOS auto-updater depend on OTA-style delivery mechanisms.
Web applications
Service Workers allow web apps to replace old files with new ones quietly — a web form of OTA.
Gaming platforms
Steam, Epic Games Launcher, Battle.net — all use OTA-like background updates.
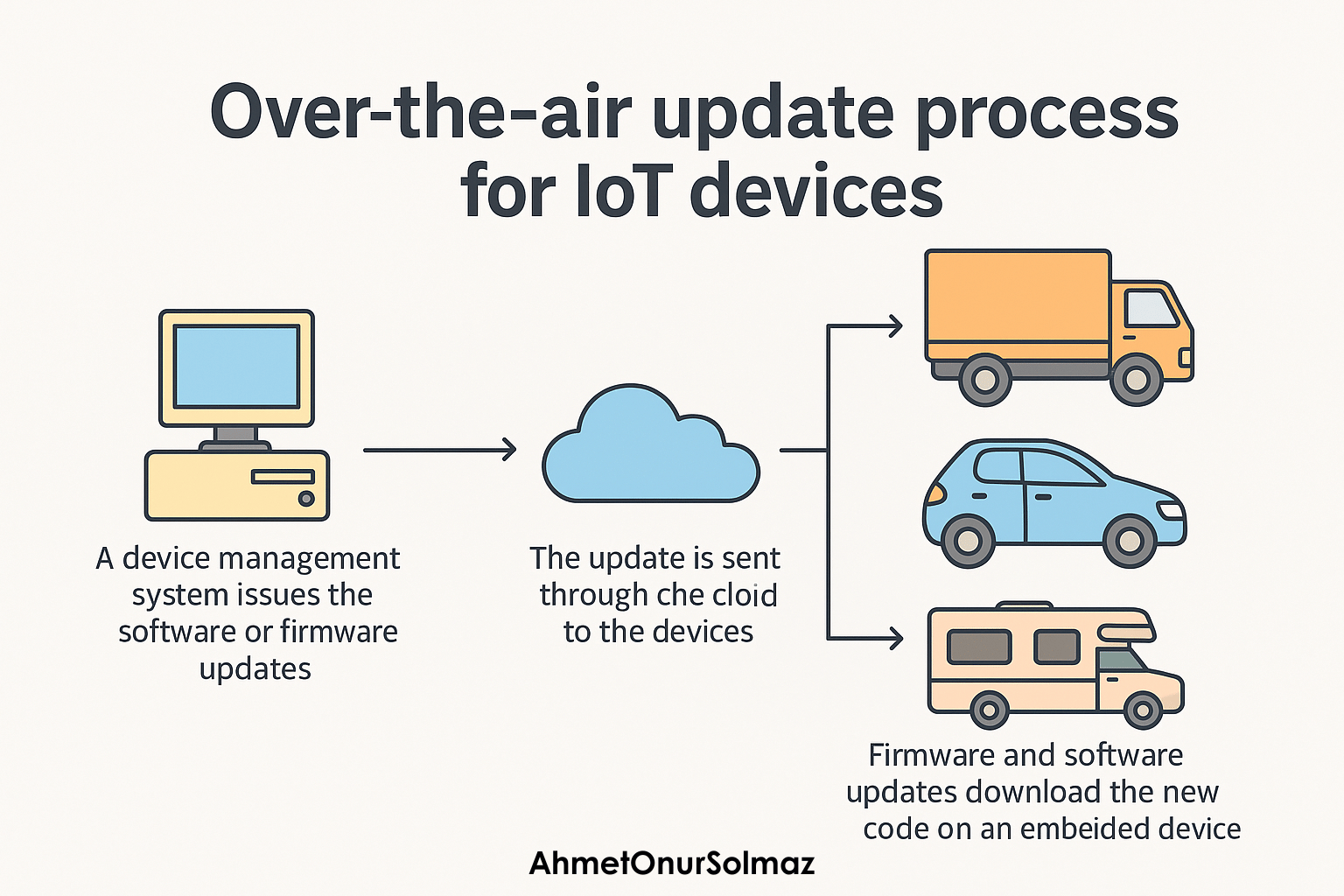
IoT devices
This is where OTA becomes essential.
Millions of devices like:
- smart thermostats,
- home assistants,
- routers,
- security cameras,
- industrial sensors
cannot be updated manually. OTA is the only scalable method for them.
For an external technical reference, you can check the Wikipedia article:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Over-the-air_update
Challenges and Best Practices in OTA Update Management
OTA is powerful, but it must be used carefully.
Security first
Every update should be:
- encrypted,
- signed,
- verified on the device before installation.
Skipping these steps can expose the entire ecosystem to attacks.
Handle poor network conditions
Not every user has stable internet.
OTA systems should include:
- resumable downloads,
- small delta update packages,
- fallback mechanisms when installation fails.
Ensure compatibility
Especially in IoT, sending the wrong update can “brick” a device — meaning it becomes unusable.
Staged rollout, version checks, and compatibility validation are essential.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-moving digital world, OTA systems help products stay secure, reliable, and continuously improving. Understanding What is OTA in software engineering gives you insight into one of the invisible forces powering modern technology.
Thanks for taking the time to read this. If you’d like to explore OTA further or discuss how to integrate it into your own product, feel free to reach out — always happy to help.
And remember: as technology continues to evolve, the answer to What is OTA in software engineering will only grow more meaningful and more essential.

Leave a Reply